Section 9: Risk Management
QUESTION 1
While preparing your risk responses, you realize that you have not planned for unknown risk events. You need to make adjustments to the project to compensate for unknown risk events. These adjustments are based on your past project experience when unknown risk events occurred and knocked the project off track. What should you do?
A. Include a management reserve in the budget to try to compensate for the unknown risks, and notify management to expect unknown risks to occur.
B. Document the unknown risk items and calculate the expected monetary value based on probability and impact that may result from the occurrence.
C. Determine the unknown risk events and the associated cost, then add the cost to the project budget as reserves.
D. With the stakeholders, determine a percentage of the known risk budget to allocate to a management reserve budget.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Notice how you have to read each choice carefully to get the correct answer? This question is asking how unknown risks are handled. It should be a reminder that, though the risk management process is designed to identify risks, not all risks can be identified. Some will inevitably remain unknown. Thus, unknown risks cannot be assessed (choice B) or identified (choice C) since they are "unknown". A management reserve is not calculated based on a percentage of known risks (choice D). The amount of known risk reserves will have
no impact on the amount of unknown risks. Past history of what projects have needed is a better indicator. A management reserve is used for unknown risks, and it is wise to inform management that unknown risks can occur, making choice A best.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 396
QUESTION 2
You have just been assigned as the project manager for a new telecommunications project that is entering the second phase of the project. There appear to be many risks on this project, but no one has evaluated them to assess the range of possible project outcomes. What needs to be done?
A. Plan Risk Management
B. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
C. Plan Risk Responses
D. Monitor and Control Risks
Answer: A
Explanation:
Did you notice that this project has already begun? Risk management is a required element of project management. You must complete the risk management process, starting with the Plan Risk Management process, making choice A the correct choice.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 381
QUESTION 3
During project executing, a major problem occurs that was not included in the risk register. What should you do FIRST?
A. Create a workaround.
B. Reevaluate the Identify Risks process.
C. Look for any unexpected effects of the problem.
D. Tell management.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Notice that this is a problem that has occurred, rather than a problem that has just been identified. Following the right process is part of professional and social responsibility. Because an unidentified problem or risk occurred, it is important to perform choices B and C. However, they are not your first choices. You might need to inform management (choice D) but this is reactive, not proactive, and not the first thing you should do.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 401
QUESTION 4
Your project team has identified dependencies on six related projects that are providing major deliverables to your project. Some of these projects have a very similar scope and may overlap with your deliverables. In light of this, which of the following processes should you be MOST concerned about?
A. Control Scope
B. Verify Scope
C. Plan Risk Responses
D. Plan Communications
Answer: C
Explanation:
The biggest concern must be the risks that other projects may cause to yours. It would be better to prevent those problems in the Plan Risk Responses process (choice C) than to just spend effort controlling scope (choice A).
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 391
QUESTION 5
Which of the following is a chief characteristic of the Delphi technique?
A. Extrapolation from historical records from previous projects
B. Expert opinion
C. Analytical hierarchy process
D. Bottom-up approach
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Delphi technique uses experts and builds to consensus; therefore, expert opinion is the chief characteristic.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 383
QUESTION 6
Monte Carlo analysis is used to:
A. Get an indication of the risk involved in the project.
B. Estimate an activity’s length.
C. Simulate the order in which activities occur.
D. Prove to management that extra staff is needed.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Notice how many choices are half right? Monte Carlo could help you know that an estimate for an activity needs to change, but not what the activity estimate should be (choice B). Monte Carlo is a simulation (choice C) but it simulates time, not order of activities. Monte Carlo can be used to prove things to management (choice D) but its main focus deals with time, not staff. Risk can be assessed using Monte Carlo analysis (choice A). By considering the inputs to the PERT estimates and the network diagram, you can obtain a better overview of the overall project risk.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 388
QUESTION 7
While planning the project, you discover that an expert resource might be available to work on your project.
However, the resource manager will not commit to the resource being on your team at the present time. The BEST thing to do would be to estimate the activity:
A. As if the expert resource were available.
B. As though you had an average resource doing the activity.
C. As if you had an inexperienced resource.
D. Using the Delphi technique.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Since there is no one individual assigned, the better estimate can be obtained using the input of multiple experts. The Delphi Technique gains a consensus of expert opinions. In this case it would be better than using an average (choice B), which is what many people choose.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 383
QUESTION 8
A project manager has just been notified of a cost increase by a seller. He looks at the contract and determines that the seller has the right to pass along this cost increase. The project manager should FIRST determine if:
A. There is a reserve to handle the change.
B. Another seller can provide it at the original cost.
C. Another activity can save money.
D. The activity is on the critical path.
Answer: A
Explanation:
If you thought choice B would be the first choice, think of how much time it would take to review a purchase order with a new seller. Choice D deals with time, not cost. Since the seller had the right to increase price, this risk should have been identified, and a reserve created.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 396
QUESTION 9
Developing alternative activity sequences is an example of:
A. Risk transfer.
B. Risk aversion.
C. Risk identification.
D. Contingency planning.
Answer: D
Explanation:
If a risk event happens, how will we deal with it and continue with the project? We may need to identify alternative ways of sequencing the work. These alternatives are described in the contingency plan.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 391
QUESTION 10
What is the expected monetary value of the decision displayed in the chart?
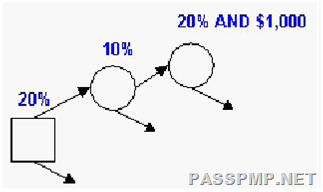
A. $4
B. $100
C. $20
D. $200
Answer: A
Explanation:
The expected monetary value is probability times impact. In this case you multiply the probabilities together and then multiply the impact. 0.20 x 0.10 x 0.20 x $1000 = $4.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 387
One thought on “PMI-001 Q&A – Section 9: Risk Management (1-10)”
Comments are closed.