Section 4: Time Management
QUESTION 41
Which of the following is the BEST method of completing “what-if” scenarios to determine what combination of resources and interdependencies will produce the best schedule?
A. Critical chain method
B. Monte Carlo analysis
C. Parametric estimating
D. Resource leveling
Answer: B
Explanation:
Notice that you need to know what each choice is in order to determine the best answer. With Monte Carlo analysis, you can perform “what-if” drills.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 211
QUESTION 42
You have a project with four activities as follows. Activity 1 can start immediately and has an estimated duration of 1. Activity 2 can start after activity 1 is completed and has an estimated duration of 4. Activity 3 can start after activity 2 is completed and has an estimated duration of 5. Activity 4 has an estimated duration of 8. It can start after activity 1 is completed. Both activity 3 and activity 4 must be completed before the project is complete. What is the critical path of the project?
A. Start, 1, 2, 3, End
B. Start, 1, 4, 3, End
C. Start, 1, 4, End
D. Start, 1, 2, 3, 4, End
Answer: A
Explanation:
The two paths you have in this question are Start, 1, 2, 3, End and Start, 1, 4, End. Path Start, 1, 2, 3, End would take 1 + 4 + 5 days, or 10 days to complete. Path Start, 1, 4, End would take 1 + 8 days, or 9 days to complete. Carefully draw the network diagram, list all the possible paths, and then determine the duration of each path.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 196-204
QUESTION 43
What is the duration of the near-critical path based on the chart?
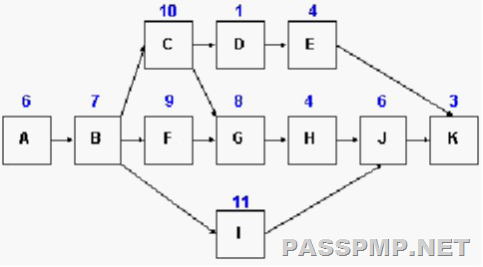
A. 33
B. 44
C. 31
D. 43
Answer: D
Explanation:
The near-critical path is the path closest in length to the critical path; in this case Start, A, B, F, G, H, J, K, End.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 196-204
QUESTION 44
An activity-on-node (AON) network diagram shows the following activities on two critical paths; Start, D, E, J, L, End and Start, D, E, G, I, L, End. Each activity is at least three days in duration, except for activity L, which is one day in duration. If you are directed to reduce the project by one day, which activities are MOST likely to change?
A. Activity L
B. Activity E or activity J
C. Activity G or activity I
D. Activity D or activity E
Answer: D
Explanation:
The activities common to the critical paths are the most likely to change; these are activities D, E, and L. However, activity L cannot change because its duration is one day and cannot be reduced to none. Therefore, the answer is choice D.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 196-204
QUESTION 45
The WBS, estimates for each work package, and the network diagram are completed. The NEXT thing for the project manager to do is:
A. Sequence Activities.
B. Develop Schedule.
C. Verify Scope.
D. Resource Simulation.
Answer: B
Explanation:
This question is asking you about the process of project management. Think about Rita’s Process Game in the book PMP® Exam Prep. Sequence Activities (choice A), has already been done in creating the network diagram. Verify Scope (choice C), occurs during monitoring and controlling. Choice D is a made-up term.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 194
QUESTION 46
A project manager is taking over a project from another project manager during the planning process group. If the new project manager wants to see what the previous project manager planned for managing changes to the schedule, it would be BEST to look at the:
A. Communications management plan.
B. Update management plan.
C. Staffing management plan.
D. Schedule management plan.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Answer D is the most correct answer. The schedule management plan is an output of Develop Project Management Plan and is the repository for plans for schedule changes. Note that choice B is a made-up term.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 181
QUESTION 47
The calculated duration of a project is 28.166. The standard deviation is 5.5. What technique would you use to compute the probability of completing a project on a specific day?
A. Reserve analysis
B. Monte Carlo analysis
C. Probability analysis
D. Variance analysis
Answer: B
Explanation:
A Monte Carlo analysis provides the ability to compute the probability of completing a project on a specific day.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 211
QUESTION 48
Based on the network diagram shown in the chart, what is the duration of the critical path?
A. 33
B. 44
C. 31
D. 36
Answer: B
Explanation:
Activities A, B, C, G, H, J, and K are activities on the critical path and their duration is 44.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 196-204
QUESTION 49
A plan for establishing the criteria for developing and controlling the project schedule is BEST described as part of the:
A. Schedule management plan.
B. Schedule model.
C. Activity attributes.
D. Schedule network analysis.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The actions being discussed are part of the schedule management plan.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 181
QUESTION 50
A project manager is using weighted average duration estimates to perform schedule network analysis. Which type of mathematical analysis is being used?
A. Critical path method
B. PERT
C. Monte Carlo
D. Resource leveling
Answer: B
Explanation:
PERT uses a weighted average to compute activity durations.
Source: PMP® Exam Prep Page: 191